Java - API & JDK
什么是 API
Application Program Interface 应用程序编程接口
整个 JKD 类库就是一个 JavaSE 的 API
每一个 API 都会配置一套 API 帮助文档
获取途径
- 源代码中(API,比较麻烦,也比较难)
- 查阅 Java 类库帮助文档
Object - JDK 类库的根类
Object 类中方法所有子类通用,任何一个类默认继承 Object 类
String toString()
将对象转换成字符串形式
类名@对象的内存地址转换为16进制形式
toString() 方法应该是一个简洁的、详实的、易阅读的
建议所有子类都重写 toString() 方法
输出对象时可以自动调用 toString() 方法
源代码
1 | |
boolean equals(Object obj)
判断两个对象是否相等
“==” 比较的是两对象内存地址,无法比较对象是否相等
源代码
1 | |
代码重写
源代码中的 equals(Object o) 默认使用 “==” 比较,无法作用于对象,所以需要重写
String
大部分情况下采用以下方法创建字符串对象:
1 | |
- 这种情况,作为 String 变量,支持使用“==”比较
String 是一个类,也可以采用构造方法创建字符串对象:
1 | |
- 字符串也属于类,这里作为 String 引用,所以无法使用“==”来比较,需要调用 equals() 方法比较
如果不知道 String 变量创建方法,建议直接使用 equals()
由于 String 类中已经重写过 equals() 与 toString(),所以可以直接调用使用
调用 equals() 时,可以优先调用字符串常量以避免空指针异常,例如
"notnull".equals(str)
String equals() 源代码
1 | |
String toString() 源代码
1 | |
protected void finalize()
protected 修饰,只有方法体没有代码,不需要手动调用,垃圾回收器负责调用的方法
执行时机
当一个 Java 对象即将被垃圾回收器回收时,垃圾回收器负责调用
该方法实际上是 SUN 公司为 Java 程序员准备的一个时机——垃圾销毁时机
如果希望在对象销毁时执行一段代码,这段代码要写到 finalize() 方法中
建议 GC 启动
System.gc();
源代码
1 | |
int hashCode()
获取对象哈希值(内存地址),返回一个 int 类型
实际上就是一个 Java 对象的内存地址,经过哈希算法得出一个值
源代码
1 | |
protected Object clone()
对象克隆
源代码
1 | |
String
java.lang.String
- String 表示字符串类型,属于引用数据类型
- Java 中使用双引号括起来的都是 String 对象
- Java 中规定,双引号括起来的字符串,是不可变的
- 在 JDK 中双引号括起来的字符串,都是直接存储在方法区的字符串常量池当中的
字符串在实际开发中使用太频繁,为了执行效率,所以放到了字符串常量池当中
字符串常量池不会被垃圾回收器回收
字符串常量池中同一个 String 的不同引用,使用 “==” 比较时返回 true,是因为双引号括起来的字符串不可变,引用的同一个字符串(new String 对象时,对象指向同一字符串,变量指向不同对象,所以使用 “==”时,前者为 true,后者为 false)
String 的构造方法
1 | |
String 类当中常用方法
char charAt(int index)
获取字符串中下标为 index 的元素
1
System.out.println("vay".charAt(1)); // aint compareTo(String anotherString)
比较两个字符串第一个不同元素 ASCII 码大小
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8System.out.println("abc".compareTo("abd")); // 前小后大
// -1
System.out.println("abc".compareTo("abc")); // 前后一致
// 0
System.out.println("abd".compareTo("abc")); // 前大后小
// 1boolean contains(CharSequence s)
判断前面的字符串中是否包含后面的字符串
1
2System.out.println("HelloWorld".contains("Hello")); // true
System.out.println("HelloWorld".contains("Hellow"));// falseboolean endsWith(String suffix)
判断当前字符串是否以某个字符串结尾
1
2System.out.println("test.java".endsWith(".java")); // true
System.out.println("text.java".endsWith(".class")); // falseboolean equals(Object anObject)
比较两个字符串或引用
1
System.out.println("abc".equals("abc")); // tureboolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)
判断两个字符串是否相等,并且同时忽略大小写
1
System.out.println("Abc".equalsIgnoreCase("abc")); // truebyte[] getBytes()
将字符串对象转换成字节数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12byte[] b = "abcdef".getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
System.out.println(b[i]);
}
/*
97
98
99
100
101
102
*/int indexOf(String str)
判断某个子字符串在当前字符串中第一次出现的索引
1
System.out.println("test.java".indexOf("java")); // 5boolean isEmpty()
判断某个字符串是否为空字符串
1
System.out.println("".isEmpty()); // trueint length()
1
System.out.println("abc".length()); // 3判断数组长度是属性,判断字符串长度是方法
int lastIndexOf(String str)
判断某个子字符串在当前字符串最后一次出现的索引(区分大小写)
1
System.out.println("learningJava.Java".lastIndexOf("Java")); // 12String replace(charSequence target, charSequence replacement)
将字符串中的 target(目标字符串)替换成 replacement(欲替换字符串)
String 的父接口就是 charSequence
1
2System.out.println("http://wataaaame.github.io".replace("http", "https"));
// https://wataaaame.github.ioString[] split(String regex)
以 “regex” 字符作为分隔符拆分字符串
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9String[] str = "2022-12-26".split("-");
for (int i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
System.out.println(str[i]);
}
/*
2022
12
26
*/boolean startsWith(String prefix)
判断字符串是否以 prefix(字符串)开始
1
System.out.println("https://wataaaame.github.io".startsWith("https")); // trueString substring(int beginIndex)
从 beginIndex(起始下标)处截取字符串
1
2System.out.println("https://wataaaame.github.io".substring(8));
// wataaaame.github.io**String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)**(方法重写)
从 beginIndex(起始下标)截取到 endIndex(结束下标)
左闭右开,可理解为光标
1
2System.out.println("https://wataaaame.github.io".substring(8, 17));
// wataaaamechar[] toCharArray()
将字符串转换成 char 数组
1
2
3
4
5char[] ch = "keep on do it!!!".toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {
System.out.print(ch[i] + " ");
}
// k e e p o n d o i t ! ! !String toLowerCase()
转换为小写
1
2System.out.println("FOR ALL THE TIME.".toLowerCase());
// for all the time.String toUpperCase()
转换为大写
1
2System.out.println("wuwuwu".toUpperCase());
// WUWUWUString trim()
去除字符串前后空白
1
2System.out.println(" space around ".trim());
// space aroundString valueOf()
将非字符串转换为字符串1
System.out.println(String.valueOf(3.14));String 中唯一的 static 方法,不需要 new 对象,使用 类名. 调用
处理对象时调用 toString 方法转换为字符串形式的内存地址
print 对象会自动调用 toString,因为 println 中会先调用 valueOf()
控制台打印的内容全都是字符串
StringBuffer & StringBuilder
StringBuffer
Java 中的字符串是不可变的,每一次拼接都会产生新字符串,这样会占用大量的方法区内存,造成内存空间浪费
所以需要进行大量字符换拼接操作,建议使用 JDK 中自带的:
java.lang.StringBuffer
java.lang.StringBuilder
- 创建 StringBuffer 时最好给定一个合适的初始化容量,以减少底层数组的扩容次数,优化性能
String 底层就是一个 private final 修饰的 byte[] 数组,所以一经创建无法改变
而 StringBuffer 底层是一个普通的 byte[] 数组,可以任意扩容
语法
创建一个初始化容量为16个 byte[] 数组(字符串缓冲区对象):
1 | |
拼接字符串统一调用 append 方法:
1 | |
指定初始化容量的 StringBuffer 对象(字符串缓冲区对象)
1 | |
StringBuilder
与 StringBuffer 类似,区别如下:
| StringBuffer | StringBuilder |
|---|---|
| 有 synchronized 关键字修饰,表示多线程安全 | 无 synchronized 关键字修饰,多线程不安全 |
基础类型对应的8个包装类
Java 中为8中基本数据类型对应准备了8种包装类型,属于引用数据类型,父类是 Object
调用方法需要传递一个数字,可是方法参数类型是 Object,无法接收基本数据类型的数字,此时就需要传递一个数字对应的包装类进去
对应的包装类型名
| 基本数据类型 | 包装类型 | 父类 |
|---|---|---|
| byte | java.lang.Byte | Number |
| short | java.lang.Short | Number |
| int | java.lang.Integer | Number |
| long | java.lang.Long | Number |
| float | java.lang.Float | Number |
| double | java.lang.Double | Number |
| boolean | java.lang.Boolean | Object |
| char | java.lang.Character | Object |
Number
是一个抽象类,无法实例化对象
将引用数据类型转换为基本数据类型(负责拆箱)的公共方法:[数据类型]Value()
示例代码
Integer 的构造方法有两个(其他的也如此):
Integer(int)
Integer(String)
此为 JDK 9 过时语法(手动装箱)
基本数据类型 -(转换为)-> 引用数据类型(装箱):
1 | |
- 123这个基本的数据类型,进行构造方法的包装达到了:基本数据类型向引用数据类型的转换
- 非数字的字符串包装成 Integer,运行会报错
引用数据类型 -(转换为)-> 基本数据类型(拆箱):
1 | |
- 默认重写了 toString() 方法
通过访问包类常量,获取数据类型的最大值与最小值:
1 | |
自动装箱 & 自动拆箱
Java 5 之后,支持自动拆箱和自动装箱,Number 类中的方法就用不着了
自动装箱:基本数据类型自动转换成包装类
Integer x = 100;
自动拆箱:包装类自动转换成基本数据类型
int y = x;
分析以下代码为何没有报错:
1 | |
- 加号两边要求是基本数据类型的数组,z 是包装类,不属于基本数据类型,这里会自动进行拆箱,将 z 转换成基本类型数据
“==” 不会触发自动拆箱机制,只有参与运算时才会触发
重要的 Integer 面试题:
1 | |
- Java 中为了提高程序的执行效率,将 [-128, 127] 之间所有的包装对象提前创建好,放到了一个方法区的“整数型常量池”中,目的是只要用了这个区间的数据不需要再 new,直接从整数型常量池当中取出来
- 原理:x 与 y 中保存的对象内存地址相同
常用方法
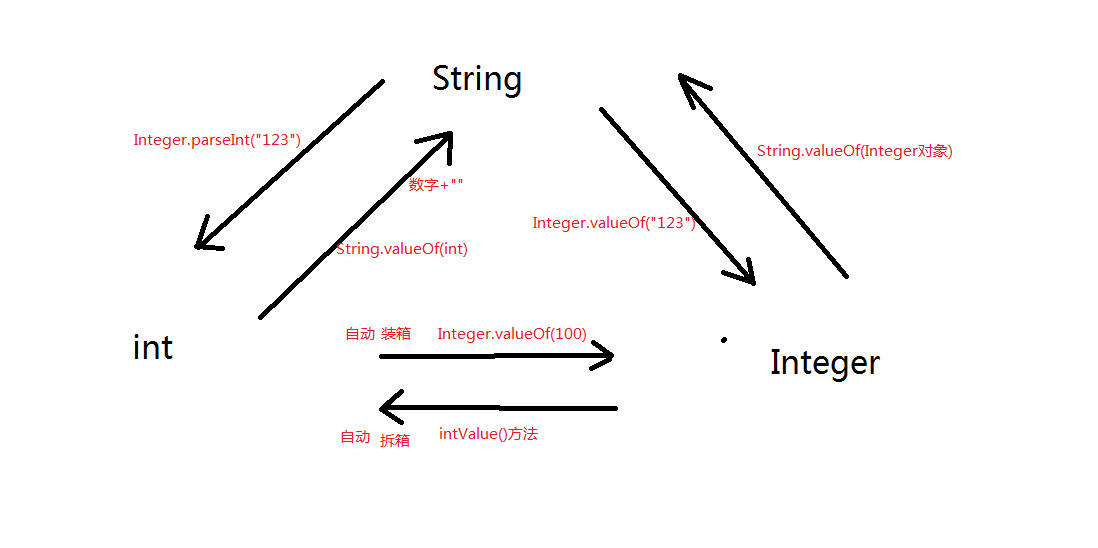
static int parseInt(String s)
静态方法,传参 String,返回 int
1
2int retValue = Integer.parseInt("123");
System.out.println(retValue + 100); // 223- 非数字字符串无法转换
类比
Double.parseDouble("3.14")Integer.valueOf([int/String])
将 int/String 数字转换成 Integer
日期相关类
java.util.Date
Date()
获取系统当前时间(精确到毫秒)
直接调用无参数构造方法
toString() 方法已被重写(国际时间格式)
1
2
3Date nowDate = new Date();
System.out.println(nowDate);
// Sun Jun 26 09:21:41 CST 2022Date(long)
表示纪元时间以后累计的时间(传入毫秒)
1
2
3Date d = new Date(1000);
System.out.println(d);
// Thu Jan 01 08:00:01 CST 1970北京是东8区,所以早8个小时
SimpleDateFormat()
java.text包下,负责日期格式化直接调用构造方法,参数列表指定日期格式
日期格式 含义 yyyy 年 MM 月 dd 日 HH 时 mm 分 ss 秒 SSS 毫秒 - 除了日期格式字母不能随便写以外,其他字符可以自定义
- 日期格式字母个数可更改
调用 SimpleDateFormat 对象的
.format(Date)来以指定格式输出 String1
2
3
4SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SSS");
String formatDate = sdf.format(nowDate);
System.out.println(formatDate);
// 2022-06-26 09:33:51:786日期字符串如 String 如何转换成 Date 类型?
使用 SimpleDateFormat 对象的
.parse(String)方法输出 Date1
2
3
4
5
6public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
String time = "2004-04-04 04:04:44:444";
SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-mm-dd HH:mm:ss:SSS");
Date d = sdf2.parse(time);
System.out.println(d);
}- 需要在方法中抛出异常
- 字符串日期格式和 SimpleDateFormat 指定的日期格式需要相同
System.currentTimeMillis();
获取自 1970年1月1日 0时0分0秒 000毫秒 到当前系统时间的的总毫秒数
1
2
3long nowTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(nowTimeMillis);
// 1656208105060可用来计算程序运行时间
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8// 统计当前系统 for 循环1000次耗费的时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("i = " + i);
}
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Using " + (endTime-startTime) + "ms");
// Using 72ms- 打印结果会大量耗费时间
数字相关类
java.text.DecimalFormat
java.text.DecimalFormat()
专门负责数字格式化
1
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("数字格式")数字符号 数字格式 # 任意数字 , 千分位 . 小数点 0 不够时补0 1
2
3
4DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("###,###.0000");
String s = df.format(1234567.891);
System.out.println(s);
// 1,234,567.8910BigDecimal
java.math.BigDecimal属于大数据,精度极高,属于 Java 对象(引用数据类型),是 SUN 提供的一个类,主要用于财务软件中(Double 精度不够)
1
2BigDecimal v1 = new BigDecimal(100);
BigDecimal v2 = new BigDecimal(200);引用不可使用运算符运算,需调用
.add()进行求和:1
2
3BigDecimal v3 = v1.add(v2);
System.out.println(v3);
// 300
Random
java.util.Random
随机数
1 | |
r.nextInt(bound):产生 [0, bound) 之间的随机数
1 | |
Quiz
生成5个不重复的随机数,放到数组中
1 | |
Enum(枚举)
返回值多于两种时,可以使用枚举类型(2种可使用 boolean)
- 枚举也是一种引用数据类型
- 一枚一枚可以列举出来的,才建议使用枚举类型
- 枚举编译后也是生成 class 文件
- 枚举中的每一个值可以看作是常量
例如:四级、星期等
1 | |
Example
随机返回周一到周日
1 | |
1 | |
- 高版本 switch 参数列表中支持:String,枚举(老版本仅支持 int)